CUTOMER SUPPORT & SALES
+ 91-9833297671 / 9819030056
+91-9833297671
INQUIRY NOW
for DOMESTIC – info@ravipharma.in
for INTERNATIONAL – exports@ravipharma.in

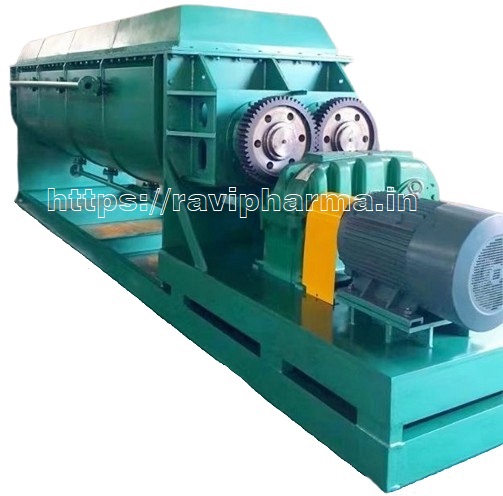
CONTINUOUS ROTARY PADDLE DRYER
Introduction and Application :-
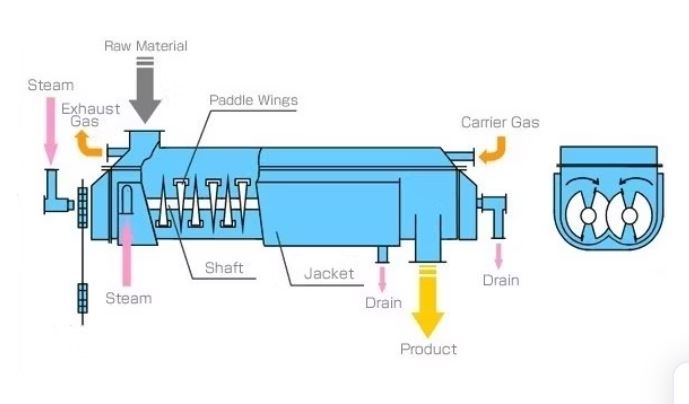
RAVI – Continuous Rotary Paddle Dryer is applied to dry or cool paste, particles, powdery materials, and slurry state materials. It performs the process of drying, cooling, heating, sterilizing, reacting and combustion under low temperature. The special agitating and heat transferring blades achieve high heat transfer efficiency and provide self-cleaning function. Paddle dryer has been successfully used in pharmaceutical, food, chemical, petrochemical, dyes, industrial sludge and other fields.
Working Principle :-
The Hollow chock shaped blades or wedge-shaped blades are concentrated on the hollow shaft. Heating media flows through the blades from the hollow shaft. The heat transfer area in the effective volume is very high. The temperature range of heating media is – 40 ºC to 300 ºC. Heating source could be steam, liquid state, such as steam, thermal oil etc.
A heating medium enters the hollow rotary shafts and paddles through a rotary feeder. After heat transfer and drying, it is discharge through the rotary discharger. The materials is continuously fed into the equipment. Next it is agitated and mixed near the paddles. At the same time, the material is gradually dried by the heat conduction of paddle and jacket. The height of overflow weir can be change to adjust residence time. In addition, steam produced in the drying process discharges through the escape hole with trace amount of air. By using oil for the heat medium, it is possible to use high temperature up to 300 Deg. C.
Slurry with high moisture content or material with high viscosity can be treated. Available under vacuumed condition as well, for materials which are sensitive to high temperature.
Indirect heating, there’s no heat carried out by air. All heat is utilized to dry the materials except the lost of heat insulation layers. The surface of chock shaped blade has self-cleaning function. The relative movements of the product particles and the chocked shaped blades surface might clean the materials attached to the blades surface, so the heat transferring surface is clean during working.
The shell of hollow blade paddle dryer is Ω shape. 2 or 4 pieces of hollow stirring shaft are usually equipped in the shell. To avoid any leakage of materials and dust, there’re sealed terminal cover and top cover with the shell. The heat transferring media flow through the rotation connector, jacket’s shell and hollow stirring shaft.
The heat transfer medium passes through the rotary joint, through the housing jacket and hollow shaft, the hollow mixing shaft in accordance with the type of the heat media has a different internal structure, to ensure optimum heat transfer effect.
- Wide Range of Applications
- Compact Structure
- Less Dust and Odor
- Strong Self-cleaning Performance
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency
- Simple and Convenient Operation
- Almost No Wear and Material Loss
CONTINUOUS ROTARY PADDLE DRYER :
Features :-
- Low energy consumption: No heat carried out by the air due to indirect heat. There’s no heat insulation layer with the exterior wall of the dryer. It consumes 1.2kg steam to evaporate 1kg water for drying slurry materials.
- Low cost of the blade dryer system: the unit effective volume has a large heat transfer surface, so the processing time is shorted; the size of the equipment becomes small. It greatly reduces the floor area and building space.
- Handling wide range of materials: Heat sensitive material and the materials to be processed under high temperature might be processed with different heating media.
- Common media are: steam, thermal oil, hot water and cooling water, etc.
- Continuous operation or intermittent batch operation, widely used in many fields.
- Environmental pollution is less: Without any carrying air, very few powders is carried out. Evaporation of the solvent material is very small, easy to handle. For the materials that might cause pollution or the solvent to be recovered, it might adopt sealed circulation.
- Stable operation: the wedge-shaped blades will do special compression, expansion of stirring effect, the material particles will fully contact with the heat transfer surface in the axial section. The difference of the temperature, humidity and mixing effect are very small in the different axial area, so to ensure the stability of process.
- Low speed will not break the granular materials or sliced materials.
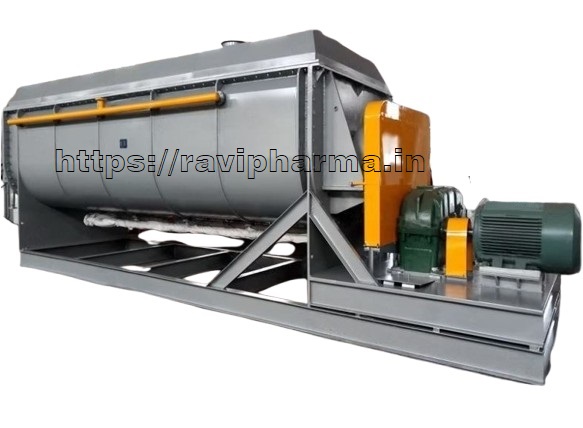
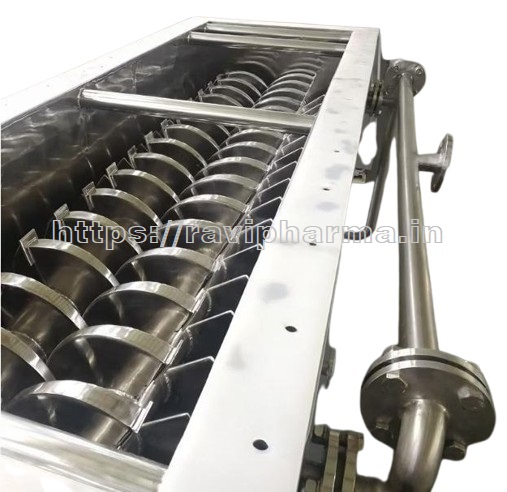


Technical Specifications:-
Continuous Rotary Paddle Dryer
Specification \ Model | CRPD-RV3 | CRPD-RV9 | CRPD-RV13 | CRPD-RV18 | CRVPD-RV29 | CRPD-R41 | CRPD-RV52 | CRPD-RV68 | CRPD-RV81 | CRPD-RV95 | CRPD-RV110 |
Heat transfer area (M2) | 3 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 29 | 41 | 52 | 68 | 81 | 95 | 110 |
Effective volume (M3) | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.59 | 1.09 | 1.85 | 2.8 | 3.96 | 5.21 | 6.43 | 8.07 | 9.46 |
Adjustable rotating speed (RPM) | 15~30 | 10~25 | 10~25 | 10~20 | 10~20 | 10~20 | 10~20 | 10~20 | 5~15 | 5~15 | 5~10 |
Power (kw) | 2.2 | 4 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 11 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 55 | 75 | 95 |
Total width of dryer (mm) | 736 | 841 | 1066 | 1320 | 1474 | 1676 | 1854 | 2134 | 1186 | 2438 | 2668 |
Total length of dryer (mm) | 2972 | 4876 | 5486 | 5918 | 6808 | 7570 | 8306 | 9296 | 9678 | 9704 | 9880 |
Distance from inlet to outlet (mm) | 1752 | 2540 | 2768 | 3048 | 3810 | 4420 | 4954 | 5384 | 5562 | 5664 | 5664 |
Total height of dryer (mm) | 762 | 838 | 1092 | 1270 | 1524 | 1778 | 2032 | 2362 | 2464 | 2566 | 2668 |
Size of steam inlet (inch) | 3/4 | 3/4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 2 |
Size of water outlet (inch) | 3/4 | 3/4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 11/2 | 2 |
Note :- We have larger or smaller models to choose from, and we can also accept customization services, please feel free to contact us.

