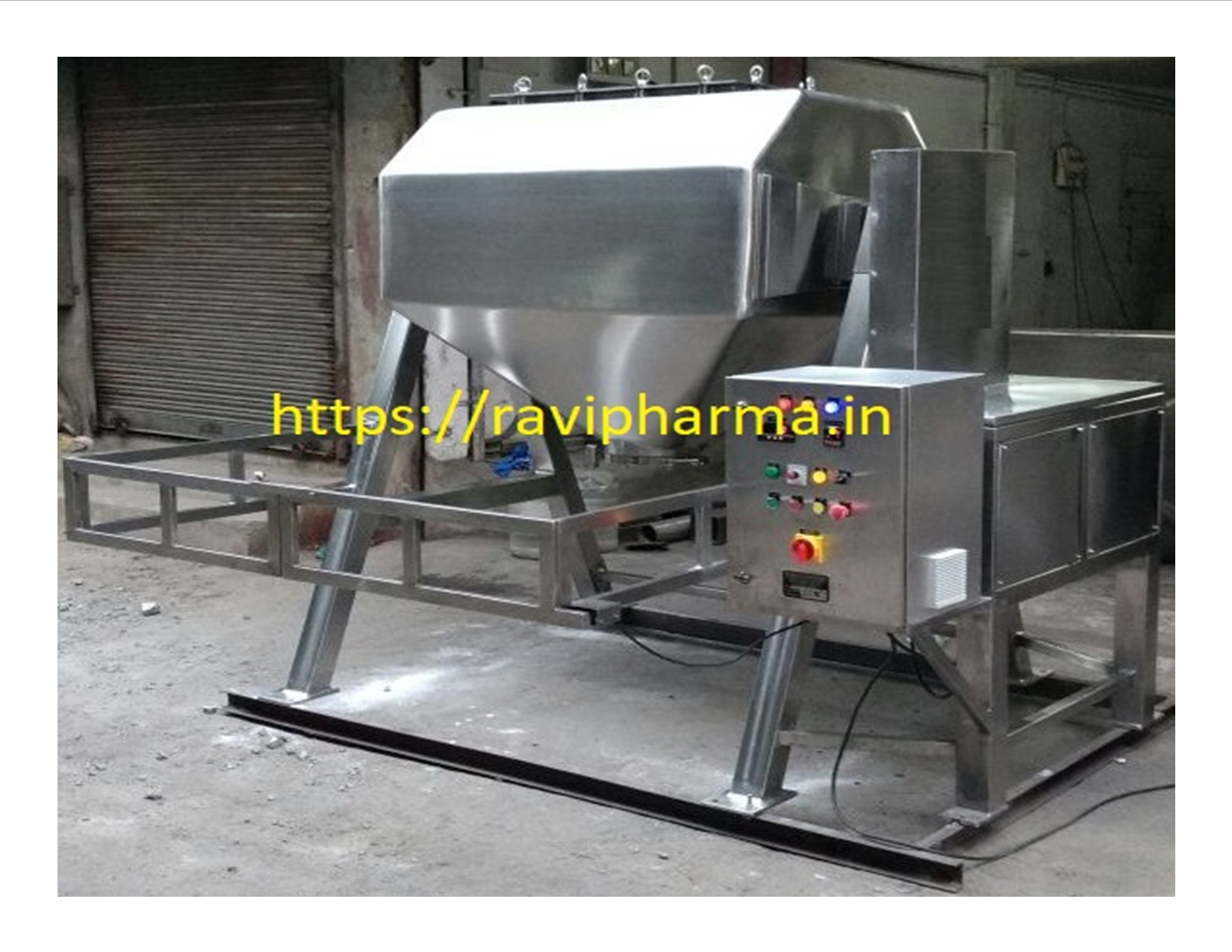
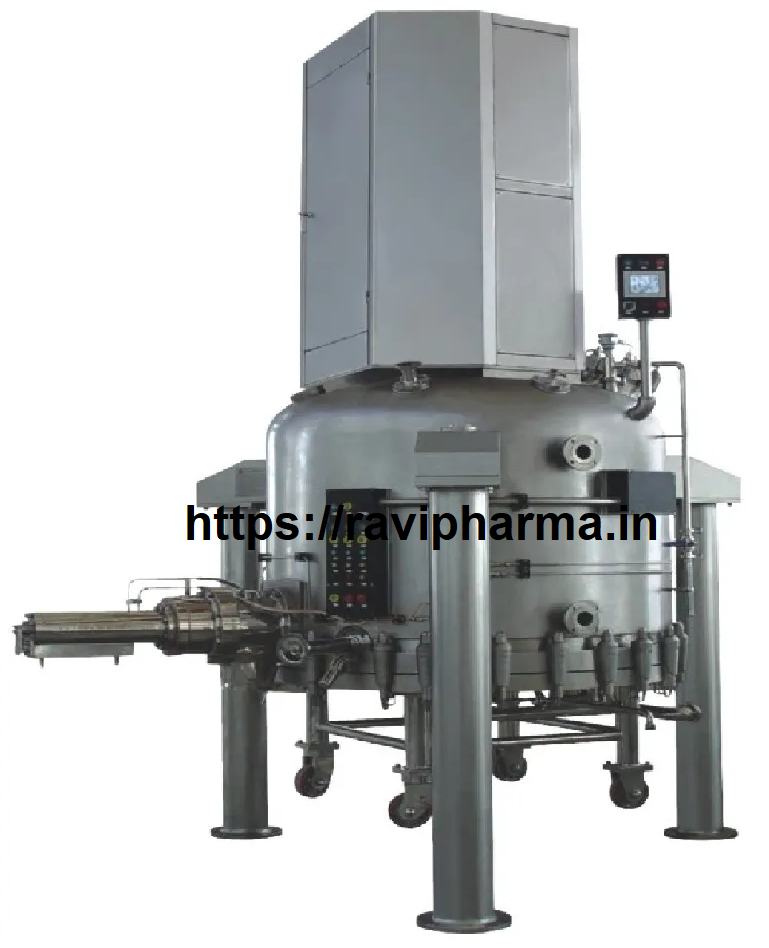
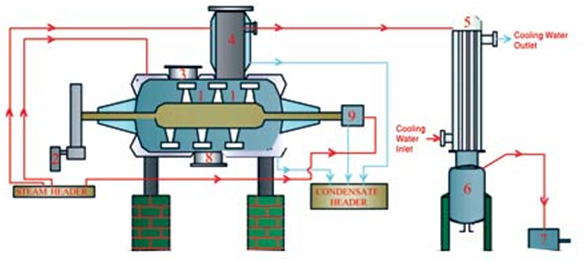
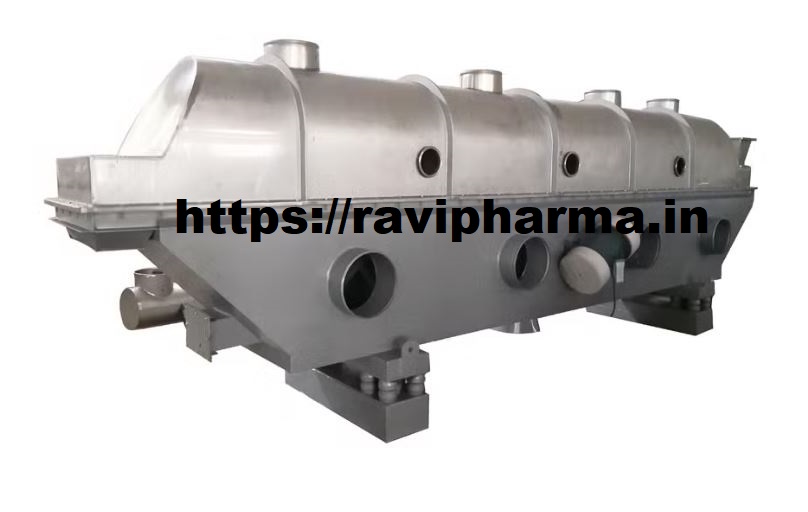
✅ Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer (CFBD) – Detailed Overview
A Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer (CFBD) is an industrial drying system widely used in pharmaceutical, chemical, food, and mineral industries. It offers consistent, efficient, and continuous drying of particulate materials.

🔑 Key Features – Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer
- Continuous operation – material enters one side, dries in the fluidized zone, and exits on the other side without interruption.
- Uniform drying – hot air fluidizes particles ensuring uniform heat transfer.
- Efficient moisture removal – reduces drying time compared to batch systems.
- Controlled environment – adjustable parameters like air temperature, flow rate, and residence time.
- Scalability – suitable for small pilot units to large industrial plants.
✅ Working Principle – Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer
- Material Feeding: Wet material (granules, powders, crystals) is fed continuously into the dryer.
- Fluidization Zone:
- Hot air passes upward through the bed of particles.
- The air flow lifts and suspends particles, creating a fluid-like behavior.
- Heat & Mass Transfer:
- Moisture evaporates from the particle surfaces.
- Hot air carries away vaporized moisture.
- Residence Time Control:
- The design ensures each particle stays in the dryer long enough for uniform drying.
- Discharge:
- Dried product exits continuously, typically via a vibrating screen or discharge outlet.
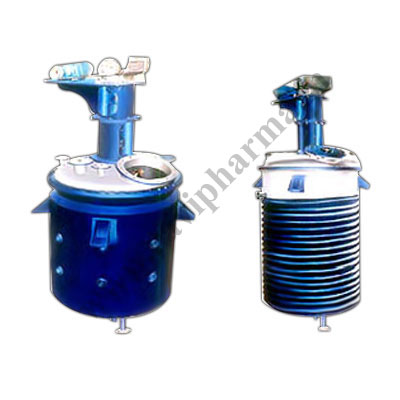
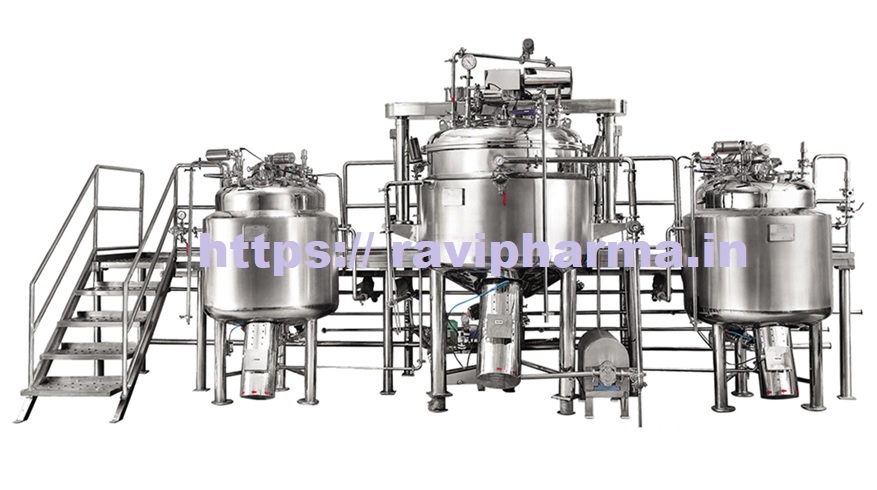
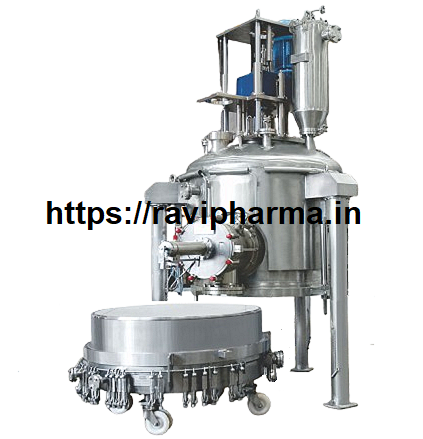
✅ Major Components
- Feed Hopper – supplies wet material.
- Fluidized Bed Chamber – where drying happens.
- Hot Air Blower – provides heated airflow.
- Distributor Plate – ensures even air distribution.
- Moisture Separator – removes entrained moisture particles.
- Discharge System – collects the dried product.
- Control Panel – regulates temperature, air flow, and other parameters.
✅ Applications
- Pharmaceuticals – drying granules, powders, active ingredients.
- Food Industry – drying grains, seeds, snacks, spices.
- Chemicals – drying catalysts, pigments, resins.
- Minerals & ceramics – drying sand, clay, minerals.
✅ Advantages
✔ High thermal efficiency
✔ Consistent product quality
✔ Reduced batch-to-batch variability
✔ Lower energy consumption
✔ Minimal manual intervention
✔ Easily automated and integrated with upstream/downstream processes
✅ Design Considerations
- Airflow rate and velocity
- Temperature uniformity
- Particle size distribution
- Bed height and length
- Moisture content before and after drying
- Product fragility (avoid attrition or breakage)
✅ Safety & Maintenance
- Ensure proper airflow to avoid dead zones or overheating.
- Install sensors for temperature and humidity monitoring.
- Regular cleaning to prevent clogging or contamination.
- Safety interlocks to prevent dry running or overheating.
✅ Comparison: Continuous FBD vs Batch FBD (and Related Variants)
| Feature / Parameter | Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer (CFBD) | Batch Fluidized Bed Dryer (Batch FBD) | Top-Spray / Bottom-Spray FBD (Granulation FBD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation Mode | Continuous | Batch | Batch or semi-continuous |
| Typical Applications | Large scale drying of powders, granules | Small to medium batch drying | Granulation, coating, drying, mixing |
| Material Feed & Discharge | Constant feed and discharge | Manual or periodic | Intermittent, with spray nozzles |
| Control of Moisture | Precise, uniform drying | Less uniform, dependent on batch size | Controlled, especially for granules or coated products |
| Process Efficiency | High | Moderate | Moderate to high depending on setup |
| Heat Transfer | Excellent fluidization heat transfer | Good but less uniform | Controlled through spray distribution |
| Automation | High | Limited | Moderate to high, depending on process |
| Scale of Operation | Industrial, large | R&D, small-medium scale | Medium scale, specialized products |
| Maintenance Complexity | Moderate | Simple but requires batch cleaning | Higher due to spray nozzles and maintenance |
| Energy Use | Efficient | Less efficient | Moderate to high depending on granulation load |
| Footprint | Compact for large volumes | Smaller footprint | Medium footprint with additional spray components |
| Product Quality | Uniform, low degradation | Variability across batches | Excellent for uniform granules, coatings |
| Process Flexibility | Less flexible (optimized for one product at a time) | High, can handle multiple products | Moderate, suited for coated or granulated products |
| Limitations | Needs continuous feed and robust process control | Downtime between batches, inconsistent quality | Sensitive to feed properties, nozzle clogging, higher complexity |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower capital cost | Moderate to high depending on granulation requirements |
✅ Key Differences Explained
1. Operation Mode
- CFBD is best for uninterrupted, high-throughput drying operations.
- Batch FBD suits smaller volumes and allows multiple formulations in separate batches.
- Top/Bottom Spray FBDs are specialized for processes like granulation or coating where spray distribution is key.
✅ 2. Product Types
- CFBD excels in drying powders, crystals, and granules with minimal degradation.
- Batch FBD is more suited for occasional drying runs, smaller-scale batches, or products that need frequent changeovers.
- Spray-based FBDs are ideal for producing coated granules, tablets, or uniform agglomerates.
✅ 3. Process Control
- CFBD allows precise control over air flow, temperature, and residence time — crucial for sensitive materials.
- Batch FBD relies on operator control; variability may occur depending on loading and time.
- Spray FBDs require control over spray rate, droplet size, and air distribution to maintain quality.
✅ 4. Maintenance & Cleaning
- CFBD has continuous operation but requires cleaning schedules and filter maintenance.
- Batch FBD requires more manual cleaning after each batch but is simpler to operate.
- Spray FBDs need maintenance of nozzles, pumps, and filters, increasing operational complexity.
✅ 5. Suitability by Industry
✔ CFBD → Large pharmaceutical, chemical, and food production lines
✔ Batch FBD → R&D labs, pilot plants, small-scale production
✔ Spray FBD → Pharmaceutical granulation, food coating, specialty powders
✅ When to Choose Which?
| Scenario | Recommended Dryer |
|---|---|
| High-volume continuous drying | CFBD |
| R&D or low-volume production | Batch FBD |
| Coating, granulation, or specific texture formation | Top/Bottom Spray FBD |
| Uniform moisture content with automated control | CFBD |
| Multiple products with frequent changeover | Batch FBD |
| Producing pellets or coated materials | Spray FBD |